Recognizing Early Signs
Recognizing the early signs of autism in babies and kids is crucial for early intervention and support. Understanding these signs can help parents and caregivers seek appropriate help and resources. Here are some key early signs to look out for:

Difficulty with Eye Contact
Children with autism may exhibit difficulties with eye contact. They may avoid making eye contact or have trouble maintaining it as usual. This difficulty in eye contact can affect their social interactions and communication skills. It’s important to note that every child is unique, and while some may struggle with eye contact, others may not. However, consistent challenges in this area can be an early indicator of autism.
Speech and Language Challenges
Another early sign of autism is speech and language challenges. Children with autism may experience delays or differences in speech and language development. They may use fewer words, have trouble communicating their needs and emotions, or exhibit repetitive or verbose speech patterns. Some children may also engage in parroting or echoing, where they repeat words or phrases they have heard, often mimicking the tone of voice. Approximately 25% of children later diagnosed with autism may experience a regression in language and social skills between the ages of 15 and 24 months.
Lack of Imaginative Play
Imaginative play is an essential aspect of childhood development. However, toddlers with autism may exhibit a lack of engagement in imaginative play activities that other children of their age enjoy. They may find it challenging to pretend, fantasize, or engage with make-believe toys. This difficulty in engaging in imaginative play can be an early indication of autism spectrum disorder.
It’s important to note that the presence of these early signs does not necessarily confirm an autism diagnosis. If you notice any of these signs or have concerns about your child’s development, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or developmental specialist for a comprehensive evaluation. Early identification and intervention play a crucial role in supporting children with autism and promoting their overall development.
Behavioral Patterns
When it comes to recognizing early signs of autism in babies and kids, it’s important to pay attention to their behavioral patterns. Two key behavioral indicators of autism are repetitive behaviors and difficulty with social interactions.
Repetitive Behaviors
Repetitive behaviors, also known as restricted and repetitive behaviors (RRBs), are common in children with autism. These behaviors may include actions like flapping or rocking, repeating words or phrases, or engaging in repetitive play with objects. RRBs are considered a core diagnostic feature of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and are prevalent early in life.
It’s important to note that while some repetitive behaviors can be a normal part of a child’s development, their frequency and intensity may be different in children with autism. Studies have shown that RRBs are more prominent and occur more frequently in autistic children compared to typically developing children and children with developmental delays. However, it’s worth mentioning that the level of RRBs does not necessarily correlate with the severity of autism in young children.
Difficulty with Social Interactions
Difficulty with social interactions is another behavioral pattern that may indicate autism in babies and kids. Children with autism may struggle with understanding and responding to social cues, making eye contact, and engaging in reciprocal conversations. They may find it challenging to initiate or sustain social interactions with peers or adults.
These difficulties in social interactions can significantly impact a child’s ability to form and maintain relationships. It’s important to observe if a child consistently exhibits social challenges that are significantly different from their peers.
Recognizing these behavioral patterns in babies and kids is crucial for early identification and intervention. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life for children with autism. Seeking professional help, such as consulting a doctor or obtaining a referral to a developmental specialist, is essential for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate support.
Understanding the behavioral patterns associated with autism spectrum disorder can help parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals identify potential signs at an early stage and provide the necessary support and interventions to promote the child’s development and well-being.
Signs in Babies
Recognizing the early signs of autism is crucial for early intervention and support. In some cases, parents may notice signs of autism in babies as early as 6 to 12 months old or even earlier. It’s important to be aware of these signs to ensure that appropriate steps are taken to address the child’s needs. Two key signs to look out for in babies include:
From 6 to 12 Months
During this period, parents may observe certain behaviors or lack of behaviors that could indicate the possibility of autism. It’s important to note that these signs alone do not necessarily mean that a child has autism, but they may warrant further evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Failing to Communicate
One of the early signs of autism in babies is a difficulty in communication through sounds or gestures. Babies typically begin to communicate their needs and wants through babbling, pointing, and making eye contact. However, babies on the autism spectrum may show delays or challenges in these areas.
By the age of 12 months, children with autism may appear to ignore their parent’s attempts to point at objects, causing concerns about their hearing. They may not respond when their name is called, and they might not engage in back-and-forth interaction, such as smiling or cooing in response to their caregiver’s social stimulation.
Additionally, by the age of 15 months, children with autism may not point to out-of-reach objects. Instead, they may take a parent’s hand and lead them to the object without making much eye contact. This lack of pointing and limited eye contact can be a red flag for further evaluation.
Around 18 months, children on the autism spectrum may point to objects, not to enjoy looking at them with a parent, but because they want the parent to get the object for them. This behavior, known as “requesting with an adult,” combined with limited eye contact, can be another sign of potential autism [2].
It’s important to note that these signs may vary among individuals and not all babies with autism will exhibit the same behaviors. If you notice any of these signs or have concerns about your baby’s development, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation.
Understanding and recognizing the early signs of autism in babies is the first step towards early intervention and support. Early diagnosis and intervention can make a significant difference in the child’s development and overall well-being. By seeking professional help and accessing appropriate resources, parents and caregivers can provide the necessary support and interventions to help their child thrive.
Importance of Early Intervention
When it comes to autism, early intervention plays a crucial role in improving outcomes for children. Research suggests that the earlier the diagnosis and enrollment in developmental and behavioral interventions, the more effective the treatments can be. Early intervention focuses on providing support and therapies to help children with autism develop to their full potential.
Benefits of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of autism allows for timely intervention, which can significantly impact a child’s development and overall well-being. Studies have shown that early interventions lead to significant improvements in cognitive, language, and social-emotional functioning in children with autism. Some of the key benefits of early diagnosis include:
- Improved Treatment Outcomes: With early diagnosis, children with autism can receive appropriate interventions tailored to their needs. These interventions might include speech therapy, occupational therapy, and mental health counseling. Evidence-based treatments can help manage symptoms and support individuals with autism throughout their lives [5].
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Early intervention aims to improve the child’s overall quality of life by addressing their specific challenges and providing the necessary support. By identifying and addressing the early signs of autism, interventions can help individuals with autism lead a more fulfilling and independent life.
Treatment and Support Options
Treatment and support options for children with autism vary depending on the individual’s needs and strengths. Early intervention programs often involve a multidisciplinary approach, including therapies and services such as:
- Speech Therapy: Speech therapy focuses on improving communication skills, including language development, social communication, and nonverbal communication.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy helps individuals develop skills necessary for daily activities, such as self-care, fine motor skills, and sensory integration.
- Behavioral Therapy: Behavioral therapy, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), is commonly used to address challenging behaviors, teach new skills, and promote positive behaviors.
- Social Skills Training: Social skills training helps individuals with autism develop social interaction skills, including understanding social cues, building relationships, and navigating social situations.
- Parent Education and Support: Providing parents with education and support is an integral part of early intervention. Parents play a vital role in their child’s development and can benefit from learning strategies to support their child’s progress.
It’s important for parents and caregivers not to delay seeking professional help if they have concerns about their child’s development. Early detection and intervention are key, as simple interventions at home can have significant benefits, especially for very young children displaying early signs of autism. Early intervention, combined with the right treatment and support, can make a positive difference in the lives of individuals with autism, allowing them to thrive and reach their full potential.
Seeking Professional Help
When parents notice possible early signs of autism in their babies or kids, it is crucial to seek professional help for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate intervention. Consulting a doctor and obtaining a referral to a developmental specialist are two essential steps in the process.
Consulting a Doctor
If parents have concerns about their child’s development, it is important to reach out to their child’s doctor for guidance and support. A doctor can provide valuable insights, conduct initial screenings, and refer the child for further evaluation if necessary. Early detection and intervention are key to ensuring that children receive the appropriate support and services they need.
Tracking developmental milestones is also important. Parents are advised to monitor milestones typically achieved by children at 9 months, 12 months, 18 months, 24 months, and 36 months. If a child is not meeting these milestones or if there are any worries, consulting a pediatrician is recommended.
Referral to Developmental Specialist
In cases where concerns about possible autism spectrum disorder (ASD) arise, parents should not hesitate to ask for a referral to a developmental specialist or contact their local early intervention program for further evaluation. Developmental specialists have expertise in assessing and diagnosing ASD and can provide a more comprehensive evaluation to determine the presence of autism and develop an appropriate intervention plan.
It’s important to note that every child is unique, and while the information provided serves as a general guide, it may not apply to everyone. Consulting with healthcare professionals will provide personalized advice and guidance regarding a child’s health and well-being. Parents should not delay seeking professional help if they have concerns about their child’s development, as early intervention can have significant benefits, especially for very young children displaying early signs of autism.
Red Flags and Diagnostic Tools
When it comes to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), early identification is key to ensuring timely intervention and support. Recognizing the red flags or early signs of autism in babies and kids is crucial for prompt evaluation and diagnosis. Additionally, screening and diagnostic tools play a significant role in the assessment process.
Early Identification
Early identification of ASD involves being aware of certain behaviors and developmental patterns that may be indicative of autism. While it’s important to note that not all children will exhibit the same signs, some common red flags to look out for include:
- Delayed or limited speech and language development
- Difficulty with social interactions and communication
- Repetitive behaviors or restricted interests
- Challenges with eye contact
- Lack of imaginative play
If parents or caregivers observe these red flags, it is recommended to consult a doctor or reach out to their child’s healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance.
Screening and Diagnostic Measures
To aid in the diagnosis of ASD, healthcare professionals utilize various screening and diagnostic tools. These tools help to gather information and assess a child’s development and behavior. Some commonly used screening and diagnostic measures include:
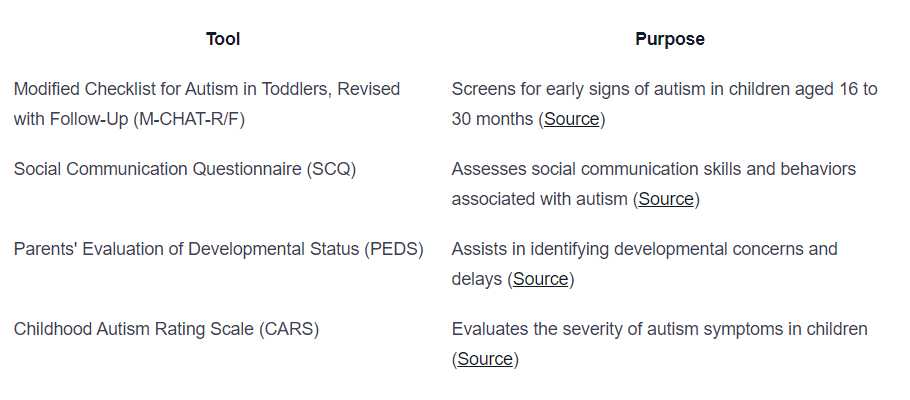
These tools, along with clinical observations and parental input, help healthcare professionals make an accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate interventions and support required.
Parents who have concerns about their child’s development should request a referral to a developmental specialist or contact their local early intervention program for further evaluation. Developmental surveillance and screening are vital in the early detection of ASD, as they involve gathering information over time from multiple sources to identify and address developmental concerns.
By being aware of the red flags and utilizing appropriate screening and diagnostic tools, parents and healthcare professionals can work together to ensure early identification, intervention, and support for children with autism spectrum disorder.
References
- https://www.goldencaretherapy.com/normal-toddler-behavior-vs-autism/
- https://www.healthychildren.org/English/health-issues/conditions/Autism/Pages/Early-Signs-of-Autism-Spectrum-Disorders.aspx
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9661964/
- https://www.readingrockets.org/topics/autism-spectrum-disorder/articles/red-flags-autism-toddlers
- https://www.parents.com/baby/health/autism/early-signs-of-autism-in-babies/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10491411/
- https://www.marcus.org/autism-resources/autism-tips-and-resources/early-signs-of-autism
- https://cps.ca/documents/position/asd-early-detection





